Working frequency of Radar
The core of radar working principle is that the radar transmits electromagnetic wave of a certain frequency, receives the echo reflected by the target, and determines some states of the target according to the echo. The frequency of electromagnetic wave emitted by radar is its working frequency.
The radar frequency band refers to the frequency range in which the radar transmits radio waves. It is measured in Hertz (Hz) or cycles per second (C/s). Most radars work in the ultrashort and microwave bands, with frequencies ranging from 30MHz to 300GHz and a corresponding wavelength from 10m to 1mm.
The specific division is as follows:
| Name | Abbre. | Freq. | Freq. Band | Freq. Length |
| Extremely low frequency | ELF | 3~30 Hz | Extremely long wave | 100kkm~10kkm |
| Super low frequency | SLF | 30~300 Hz | Super long wave | 10kkm~1kkm |
| Ultra-low frequency | ULF | 300~3000 Hz | Ultra-long wave | 1000km~100km |
| Very low frequency | VLF | 3~30 KHz | Very long wave | 100km~10km |
| Low frequency | LF | 30~300 KHz | Long wave | 10km~1km |
| Medium frequency | MF | 300~3000 KHz | Medium wave | 1km~100m |
| High frequency | HF | 0.3~30 MHz | Short wave | 100m~10m |
| Very high frequency | VHF | 30~300 MHz | Metric wave | 10m~1m |
| Ultra-high frequency | UHF | 0.3~3 GHz | Decimeter wave | 1m~10cm |
| Super high frequency | SHF | 3~30 GHz | Centimeter wave | 10cm~1cm |
| Extremely high frequency | EHF | 30~300 GHz | Millimeter wave | 10mm~1mm |
| To high frequency | THF | 300~3000 GHz | Decimillimeter wave | 1mm~0.1mm |
| Wave band symbol | Frequency Range (GHz) | Wave length range (mm) |
| UHF | 0.3~1.12 GHz | 1000~267.9 mm |
| L | 1.12~1.7 GHz | 267.9~176.5 mm |
| LS | 1.7~2.6 GHz | 176.5~115.4 mm |
| S | 2.6~3.95 GHz | 115.4~75.9 mm |
| C | 3.95~5.85 GHz | 75.9~51.3 mm |
| XC | 5.85~8.2 GHz | 51.3~36.6 mm |
| X | 8.2~12.4 GHz | 36.6~24.2 mm |
| Ku | 12.4~18 GHz | 24.2~16.7 mm |
| Ka | 26.5~40 GHz | 11.3~7.5 mm |
| Q | 30~50 GHz | 10.0~6.0 mm |
| U | 40~60 GHz | 7.5~5.0 mm |
| M(V) | 50~75 GHz | 6.0~4.0 mm |
| E | 60~90 GHz | 5.0~3.3 mm |
| W | 75~110 | 4.0~2.7 mm |
| F | 90~140 GHz | 3.3~2.1 mm |
| D | 110~170 GHz | 2.73~1.76 mm |
| G | 140~220 GHz | 2.1~1.4 mm |
| R | 220~325 GHz | 1.4~0.9 mm |
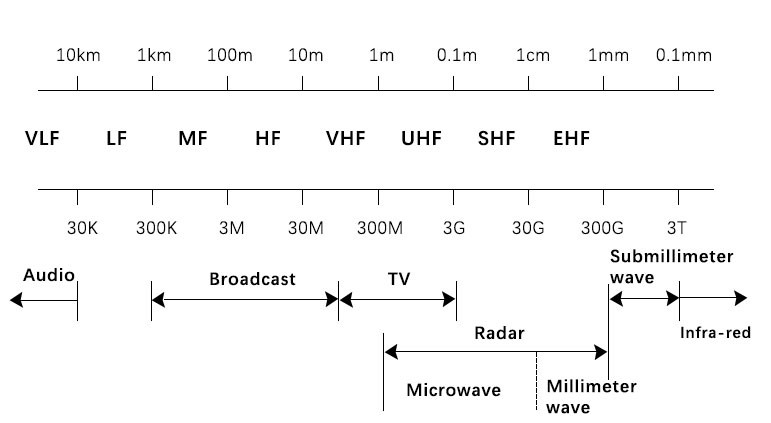
The wavelengths of radars in different bands are different:
1, Short wavelength: high resolution, poor penetration and easy to be absorbed;
2, Long wave length: low resolution and strong penetration.
Radar functions in different bands:
Search radar: working frequency band (VHF, UHF, L) ;
Search and tracking radar: working band (L, S, C) ;
Fire control radar / Imaging radar: working band (C, X, Ku) ;
Missile carrier radar: working band (X, Ku, K, Ka, V, U, W) .
Radar frequency selection:
Although radar can work in a wide frequency range, different frequencies have different working characteristics and are suitable for different purposes. Therefore, the frequency must be carefully selected when designing a radar.
Radar frequency has obvious influence on radar performance such as antenna transmit gain, antenna effective receiving area (at a certain transmit gain), transmit power, receiver noise, propagation loss, meteorological echo etc. This matters a lot when choosing the type of radar and its important indicators such as action distance, accuracy, resolution, anti-interference ability, volume weight, mobility, cost and so on.
Therefore, the radar frequency is the most important parameter of the radar parameters.




